Sundaeswap is a decentralized exchange(DEX) built on the Cardano blockchain. It allows participants to provide liquidity and create a market for others to exchange their native tokens. In return, swappers pay a small fee and liquidity providers earn a return on their deposit. It is set to launch in early December 2021.
Opportunity
Despite having smart contract functionalities, the Cardano ecosystem is a sleeping giant. Its growth hinges upon two milestones. 1) The release of a decentralised exchange. 2) The release of a stablecoin. Sundaeswap is set to be the premiere DEX on the Cardano ecosystem due to its huge community support, partnerships as well as team capability. In terms of development progress, it has released several technical updates, detailing its solution to the Cardano concurrency issue. It has also done a live swap demo on YouTube.
The sundae token will be a fairlauch token, there will not be an ICO/IDO. There are three official ways to obtain the token. They are:
- Stake ADA during its initial stakepool offering.
- Provide liquidity to Sundaeswap at launch.
- Swap for Sundaeswap tokens at launch.
However, there might be a way to obtain Sundae tokens through Cardstarter.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cz-EDAjG3vk&ab_channel=CryptoCapitalVenture
Product analysis
Sundaeswap uses a constant product market maker similar to Uniswap V1. It is a mediator between users seeking to exchange tokens as well as liquidity providers seeking to earn ecosystem rewards.
Liquidity farming
For each token pair, liquidity providers deposit an equal value of both tokens. Assuming that BTC has a value of $50,000 and ETH has a value of $5,000. A liquidity provider would need to deposit $50,000 worth of BTC(1BTC) and $50,000 worth of ETH(10ETH) as a liquidity pair. In exchange, he is given a liquidity pool token(LP token) representing his contribution. He would be able to redeem the LP token for his initial capital contribution later on. The LP token can then be staked to earn rewards. This process is known as “liquidity farming”.
Exchange
The exchange is a constant product market maker consisting of liquidity pools of two tokens. In the example above, the pool would consist of BTC and ETH. It would follow the equation:
1BTC * 10ETH = 10
(X * Y = K)
Where K is a constant product that will always stay the same, unless new liquidity is added. It follows the curve (X*Y=K) where the exchange rate will always move along the curve.
In the event that a user swaps BTC for ETH, the price of ETH increases, shifting the exchange rate to the right.
For a given trade size, a smaller pool will have higher slippage, while a larger pool will have a lower slippage. Therefore it is beneficial to aggregate as much liquidity as possible to give participants the most efficient trades.
Concurrency issue
Cardano uses an extended unspent transaction output(EUTXO) model similar to Bitcoin. Each output transaction is used as inputs for a new transaction. Ethereum, in contrast, chose to keep track of a (global) set of account balances: the ledger state is a mapping from address to balance, and a simple transaction increments and decrements account balances in pairs.
(Cardano) (Ethereum)
A few issues exist with the Ethereum model. First, every transaction must be sequenced and processed in order, since it is difficult if not impossible to determine which transactions may try to touch the same piece of state. If one transaction updates your account balance at the same time as another one, you could inadvertently destroy tokens, double-spend, and other nasty bugs.
Second, as a consequence of the above, the ordering of transactions matters, which fundamentally gives the entity ordering those transactions a lot of power. This leads to undesirable phenomena including Miner Extractable Value (MEV) and front-running.
Third, this model fundamentally requires a sacrifice of determinism, and thus demands greater trust. Because the state of the blockchain could change between when you construct your transaction and when you submit it, the smart contract needs to be trusted to do “what’s in your best interest” when it runs, even if that isn’t what you intended. For example, a DEX needs to know that if the price has moved by a certain large percentage, then you are no longer interested in the trade. A huge amount of development effort, source of bugs, and attack surface area for hacks comes from this, as each smart contract needs to be trusted to check all of the “right” invariants.
The main problem is that Ethereum makes this choice of globalizing state for every dApp, and so all of them suffer the increased transaction costs, vulnerability to front-running, and additional development burden.
Ethereum is decent at concurrency, terrible at parallelism. The UTXO model is fantastic at parallelism, but could face contention, making it not very concurrent, for some protocol designs.
Misconception 1: Cardano is flawed because it only allows 1 transaction per block.
In fact, it is quite the opposite. Cardano allows many hundreds of transactions per block. Instead, it is accurate to say that Cardano allows a given transaction output to be spent a single time, by a single transaction, so protocols that give multiple people access to the same UTXO might face contention issues
Misconception 2: Only one user can interact with a smart contract per block/transaction.
Also not true; the point of contention is around the UTXO, but many UTXOs may be governed by the same smart contract. This fundamentally comes down to the shift in thinking from Ethereum, where you call into a smart contract to make it do something, and Cardano where you lock outputs with a contract, which determines when they can later be spent.
Misconception 3: The only way to solve this is through centralization.
Source:https://sundaeswap.finance/posts/concurrency-state-cardano
Concurrency solution: Scooper model(AMM - Orderbook)
Like a pure orderbook, market participants can place good-until-canceled orders onto the blockchain. These don’t require interacting with any pre-existing entities, and so don’t suffer from the UTXO contention problems in other protocol designs. Using a programmable API, these orders can be tailored to the market participants desires. These orders are aggregated by scoopers into transactions(currently 10 orders can be aggregated into one transaction), then fitted onto the blockchain. These transactions are then executed in the AMM with their outputs distributed to individuals.The scooper can then claim a small amount of ADA rewards previously locked in a smart contract. The onchain smart contracts maintains custody of funds instead of the scoopers.
Source:https://sundaeswap-finance.medium.com/sundaeswap-labs-presents-the-scooper-model-678d6054318d
Oracle
Sundaeswap Labs is set to develop one of the first Oracle solutions on the Cardano blockchain with the help of Liqwid. This is expected to happen in later parts of 2022.
Wallets
Sundaeswap has successfully integrated the premiere Cardano wallet Yoroi as well as Namiwallet.
Initial stakepool offering(ISO)
Instead of a traditional ICO, Sundaeswap is set to conduct a stakepool offering. Where ADA holders will be able to delegate to designated stakepools. Delegators would receive their regular ADA rewards on top of Sundaeswap tokens. 200million tokens will be distributed over 5 Cardano epochs(25 days). Stakers require a minimum of 10 ADA to enter the ISO. However, it is estimated to attract immense interest from the community, thus severely diluting the rewards. Meld attracted half a billion ADA during its stakepool offering. Assuming a similar amount for Sundaeswap, The expected reward would be 0.36 Sundae per ADA staked for the full 25 days.
Competitors
From publicly available information, it seems that Sundaeswap is ahead of its competitors. We have identified the top 5 competitors: Cardax, Adax, Minswap, Ergodex and OccamX.
Cardax
Cardax is a DEX with the extended automated market maker model(EAMM). In its whitepaper, it is described as combining the best traits of the orderbook model common to CEXes and the AMM model common to DEXes. The underlying mechanisms of the protocol are not yet revealed. In terms of development progress, there hasn't been much information, unlike competitors who have had live swap demos. It has delayed its launch to Q1 2022.
Adax
Adax is a DEX with a Constant product market maker, similar to uniswap V2. It has a few partnerships such as Gerowallet, Vyfinance and C3. In terms of development, Adax has released a product demo video.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JswnyEvZYzQ&t=38s&ab_channel=ADAX
Minswap
Minswap is a DEX with constant product market makers. There has been some controversy regarding minswap with the biggest being the concurrency issue during its public testnet launch. Users received error messages while trying out swaps. This is a key concern.
Ergodex
Ergodex is a strong contender in the Cardano DEX space. Its advantage being an experienced development team who previously worked on Ergo.
OccamX
OccamX is a strong contender in the Cardano DEX space. One important advantage is that it has a sister launchpad:OccamFi. It is assumed that the projects launched from OccamFi will have their liquidity hosted on OccamX. It has also published its solution to the concurrency solution and had a live DEX demo on youtube.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qln1TupBLH4
Fundamental analysis
Sundae token
Total Supply: 2 billion
Public: 55% (1,100,000,000 tokens)
Team: 25% (500,000,000 tokens)
Investors: 13% (260,000,000 tokens)
Future Hires: 5% (100,000,000 tokens)
Advisors: 2% (40,000,000 tokens)
Traffic
Google trends
Due to the niche nature of Cardano DEXes, google trend results are not fantastic.
Similarwebs
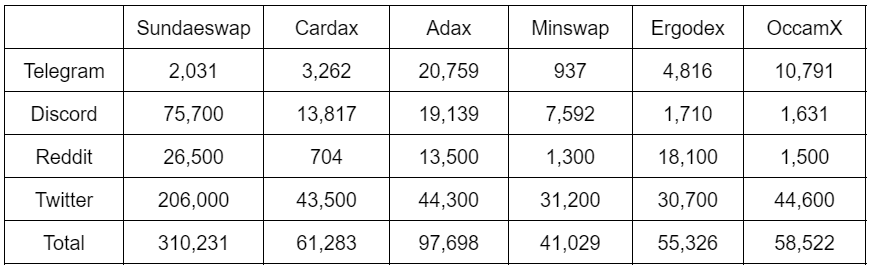
Social media members/followers
In terms of social influence, Sundaeswap is the top, followed by Adax and Cardax.
Team
The Sundaeswap team consists of a mixture of new faces and industry veterans. Members of the leadership team seem rather inexperienced. However, this is balanced out by veterans such as Matt Ho who founded three tech and finance companies. As well as the advisor: Emily pillmore, who is the CTO of the Haskell foundation.
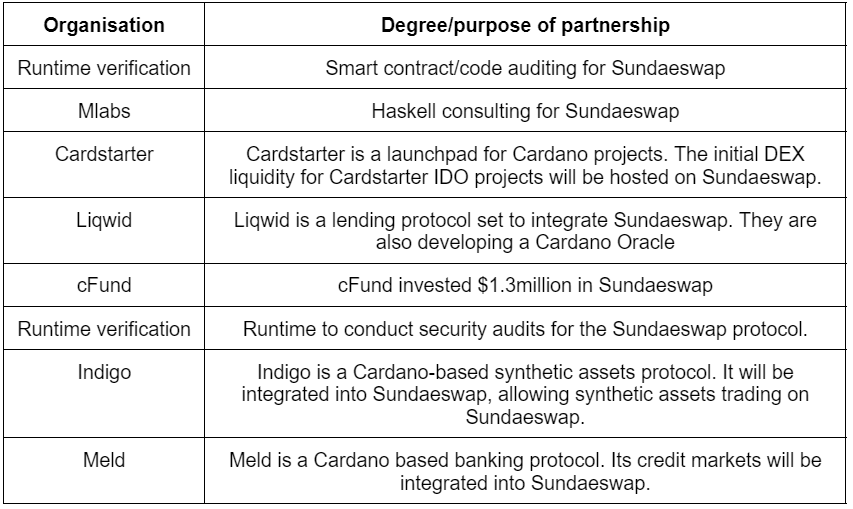
Partnerships
Sundaeswap has partnerships with key players in the Cardano ecosystem.
Inside scoop
Cardstarter is a launchpad in the Cardano ecosystem. It had the intention of creating its own DEX: Cardswap. However in July, it decided to discontinue Cardswap development and partner with Sundaeswap instead. Projects launched from cardstarer would have their liquidity hosted on Sundaeswap. That brings into question: What would happen to existing Cardswap tokens that have been issued through liquidity mining?
According to the core Carstarter team, existing Cardswap tokens will “accrue significant benefits in the Sundae ecosystem. This has been speculated to be in some form of exchange into Sundae tokens. Teams from both protocols cannot disclose the details due to an NDA. This NDA was put in place due to regulatory concerns of being classified as a securities offering, since Sundaeswap is based in the US.
Cardswap holders will have 10% of their “benefits” unlocked at the time of bridging to ADA, and the remaining 90% vested monthly for 6 months thereafter.
Alternatively, investors can provide locked liquidity for the pairs Cards-Eth, C3-Eth, Gero-Eth through the Cardano migration. They would receive Cards-ADA, C3-ADA, Gero-ADA LP tokens once the migration is complete. This in the process earns cardswap as reward.
https://cardstarter.medium.com/cswap-migration-update-50143d5efae7

